Nature's Medicines NCERT Solutions | Communicative English for Class 10 PDF Download
Textual Exercises
E1. Read the following article “Nature’s Medicine Chest” and complete the exercise that follows.
Ans: Students to read the text on their own. The textual exercise has completely been solved hereunder.
E2. Some sub-titles are given below corresponding to each of the paragraphs of the article that you have just read. Match the sub-titles with their paragraphs by writing the number of the paragraph in the space provided. Ans:
Ans:
Paragraph Numbers
- 7
- 1
- 3
- 5
- 8
- 4
- 6
- 2
E3. Find words from the passage that mean the same or nearly the same as the following:
(a) filled with a certain quality ( para 1 ) : ___________
(b) scented or perfumed or sweet-smelling (para 2) : ___________
(c) written work dealing with a subject systematically (para 3): ___________
(d) people living at the same time as others (para 5) : ________
(e) notably large or significant (para 5 ) : ____________
Ans:
(a) imbued
(b) aromatic
(c) treatise
(d) contemporaries
(e) considerable
E4. Complete the following sentences on the basis of your reading of the text in D1.
(a) After the Renaissance, the major shifts that occurred in the approach towards herbal plants were ________________ .
(b) Isolation of compounds from plants to be used as drugs was the _______________ .
Ans:
(a) the coming to the fore discoveries and inventions, rejection of alchemist’s elixirs and other magical remedies. Local plants were carefully collected and widely used to make infusions, decoctions and ointments.
(b) isolation of morphine from the opium poppy in 1803 and caffeine from coffee beans in 1819. It was also the quinine from cinchona bark, colchicines from meadow saffron both in 1820 and atropine from deadly nightshade in 1835.
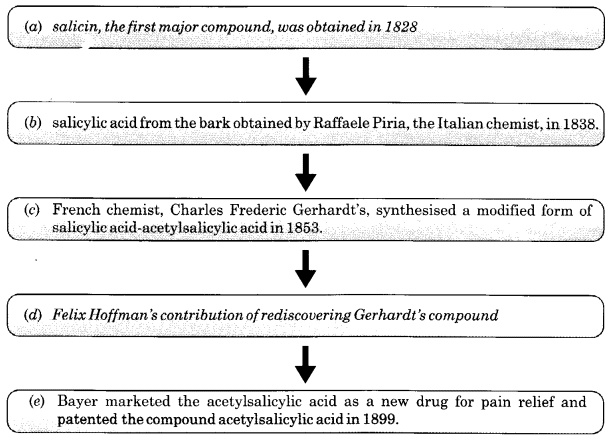
E5. Complete the following flowchart that traces the contributory processes leading to the development of the first modern drug from the willow tree. Ans:
Ans:
E6. Class Project
Work in groups of 6-8 students to present your findings on any two of the herbal plants suggested below through a series of charts or a computer power point presentation.
(a) Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
(b) Aloe vera
(c) Arnica (Arnica montana)
(d) Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)
(e) Papaya (Carica papaya)
(f) Lavender (Lavandula officinalis)
(g) Black Radish (Raphanus sativus niger)
(h) Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo)
(i) Pineapple ( Ananas comosus)
(j) Peppermint (Mentha x. peperita)
Please ensure that the whole class is divided into 4-5 groups and each group must work on different sets or pairs of herbal plants.
Ans: Class Activity
|
8 videos|250 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Nature's Medicines NCERT Solutions - Communicative English for Class 10
| 1. What are the key features of nature's medicines discussed in the NCERT Class 10 chapter? |  |
| 2. How do plants contribute to the field of medicine according to the NCERT Class 10 curriculum? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of biodiversity in the context of nature's medicines? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the traditional practices of using nature's medicines highlighted in the chapter? |  |
| 5. What role does modern science play in the validation of traditional medicines? |  |





















